Blood in Urine: Causes, Symptoms, and When to See a Doctor
Introduction
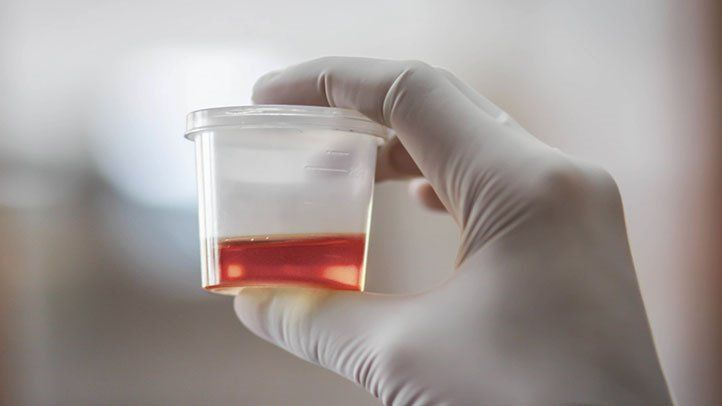
Hematuria (hee-muh-TOOR-ee-uh) is the medical term for the presence of blood cells in urine.
It’s relatively common and doesn’t always change the color of your urine. In some cases, the amount of blood is so small that it’s invisible to the naked eye and is only detected during a urine test.
However, if you notice your urine appearing pink or red, or experience other symptoms of hematuria, it could indicate an underlying health issue. In such cases, it’s important to contact a healthcare provider.
Blood in the urine, also known as hematuria, can be a sign of various underlying conditions, ranging from minor to serious. While it doesn’t always indicate a severe problem, it’s crucial to seek medical advice to determine the cause and appropriate treatment. Common causes include urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, and an enlarged prostate in men. More serious causes can include kidney or bladder cancer.
What is Blood in Urine (Hematuria)?
Hematuria, also known as blood in the urine, is the presence of red blood cells in the urine. It can be visible to the naked eye (gross hematuria) or only detectable under a microscope (microscopic hematuria). While often not a serious issue, hematuria can sometimes indicate an underlying medical condition and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Blood in urine refers to the presence of red blood cells (RBCs) in the urine. It can be visible to the naked eye, called gross hematuria, or detectable only under a microscope, called microscopic hematuria.
- Gross hematuria: Urine appears pink, red, or cola-colored.
- Microscopic hematuria: Blood is present but urine looks normal; detected via lab tests.
Common Causes of Blood in Urine
Blood in the urine, also known as hematuria, can stem from various causes, including infections, kidney stones, and certain medical conditions. Urinary tract infections (UTIs), especially bladder infections (cystitis), are a common culprit, often accompanied by pain or a burning sensation during urination. Kidney stones, which are hard mineral deposits, can also cause blood in the urine, potentially due to the stones irritating or scratching the urinary tract lining. Additionally, kidney disease, prostate issues (particularly in older men), and even strenuous exercise can lead to hematuria.
Blood in urine can stem from a variety of causes ranging from benign to serious:
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) Bacteria infecting the bladder, kidneys, or urethra can cause inflammation and bleeding. UTIs are common and often cause burning during urination, frequent urges, and cloudy urine.
2. Kidney Stones Sharp, hard mineral deposits can irritate or scratch the urinary tract lining, causing bleeding and severe pain.
3. Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) In men, an enlarged prostate can press on the urethra and cause blood in urine, often with urinary frequency and urgency.
4. Bladder or Kidney Infections More serious infections can cause hematuria alongside fever, chills, and pain in the back or sides.
5. Injury to the Urinary Tract Physical trauma from accidents, catheter use, or medical procedures can cause blood to appear in urine.
6. Kidney Disease Conditions such as glomerulonephritis cause inflammation of kidney filters, leading to microscopic or gross hematuria.
7. Cancer Bladder, kidney, or prostate cancer can cause painless blood in urine, especially in older adults and smokers.
8. Medications Blood thinners like aspirin, warfarin, or certain antibiotics can lead to bleeding.
9. Strenuous Exercise Rarely, intense exercise can cause temporary hematuria, sometimes called “runner’s hematuria.”
Symptoms Associated with Blood in Urine
These symptoms may include pain or burning during urination, a frequent or urgent need to urinate, pain in the abdomen, lower back, or side, and changes in urine color (pink, red, or brown). Some individuals may also experience fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, or fatigue.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
Urinary Symptoms:
- Pain or burning during urination: This is a common symptom, particularly in cases of urinary tract infections (UTIs) or bladder infections.
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate: This can be a sign of inflammation or irritation in the urinary tract.
- Difficulty or straining during urination: This can occur with prostate issues or urinary tract obstructions.
- Feeling like the bladder is not empty after urination: This can be associated with bladder problems or incomplete emptying.
- Changes in urine color: Pink, red, or brown urine indicates the presence of blood.
Other Symptoms:
- Pain in the abdomen, lower back, or side: This can be a sign of kidney stones, kidney infections, or other urinary tract issues.
- Fever and chills: These can indicate an infection, such as a kidney infection.
- Nausea and vomiting: These may occur with more severe infections or kidney problems.
- Fatigue and weakness: These can be associated with various conditions causing blood in the urine.
When should I see a healthcare provider?
Contact a healthcare provider if the water in your toilet looks pink or red after you pee.
But some types of hematuria aren’t obvious. In those cases, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider if you have symptoms that relate to hematuria, like:
- Changes to your peeing habits
- Signs of infection
- Pain in your abdomen, lower back or flanks
If any of your symptoms are severe, you should visit urgent care.
What questions should I ask a healthcare provider?
You may wish to ask a healthcare provider the following questions:
- What type of hematuria do I have?
- What tests do you recommend to diagnose hematuria?
- What’s causing blood in my pee?
- Do I need treatment?
- If I need treatment, what do you recommend?
- What should I do if I get blood in my pee again?
Conclusion
Blood in urine is a sign that your urinary system needs attention. While sometimes harmless, it can also indicate serious conditions such as infections, stones, or cancer. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the possible causes, and seeking timely medical advice can make a significant difference in outcomes.
If you notice blood in your urine, don’t ignore it, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to get the right diagnosis and treatment.
FAQ:
Q1: Can blood in urine go away on its own?
Sometimes, especially if caused by minor injury or exercise. But persistent or unexplained blood should always be evaluated by a doctor.
Q2: Is blood in urine always a sign of cancer?
No. Many benign conditions cause hematuria, but cancer is a serious cause that must be ruled out.
Q3: Can women get blood in urine during menstruation?
Yes. Menstrual blood can mix with urine and mimic hematuria, so timing of symptoms matters.
Q4: Does blood in urine always cause pain?
No. Blood can appear with or without pain depending on the cause.
Q5: Are there home remedies for blood in urine?
Home remedies won’t treat serious causes. Drinking water and avoiding irritants can help with minor issues, but medical evaluation is essential.



